Researchers may have accidentally discovered how to regrow hair
19 Feb 2011
It has been long known that stress plays a part not just in the graying of hair but in hair loss as well. Over the years, numerous hair-restoration remedies have emerged, ranging from hucksters' "miracle solvents" to legitimate medications such as minoxidil. But even the best of these have shown limited effectiveness.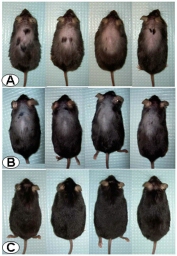 Now, a team led by researchers from UCLA and the Veterans Administration that was investigating how stress affects gastrointestinal function may have found a chemical compound that induces hair growth by blocking a stress-related hormone associated with hair loss - entirely by accident.
Now, a team led by researchers from UCLA and the Veterans Administration that was investigating how stress affects gastrointestinal function may have found a chemical compound that induces hair growth by blocking a stress-related hormone associated with hair loss - entirely by accident.
The serendipitous discovery is described in an article published in the online journal PLoS One.
"Our findings show that a short-duration treatment with this compound causes an astounding long-term hair regrowth in chronically stressed mutant mice," said Million Mulugeta, an adjunct professor of medicine in the division of digestive diseases at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA and a corresponding author of the research. "This could open new venues to treat hair loss in humans through the modulation of the stress hormone receptors, particularly hair loss related to chronic stress and aging."
The research team, which was originally studying brain – gut interactions, included Mulugeta, Lixin Wang, Noah Craft and Yvette Taché from UCLA; Jean Rivier and Catherine Rivier from the Salk Institute for Biological Studies in La Jolla, Calif.; and Mary Stenzel-Poore from the Oregon Health and Sciences University.
For their experiments, the researchers had been using mice that were genetically altered to overproduce a stress hormone called corticotrophin-releasing factor, or CRF. As these mice age, they lose hair and eventually become bald on their backs, making them visually distinct from their unaltered counterparts.
The Salk Institute researchers had developed the chemical compound, a peptide called astressin-B, and described its ability to block the action of CRF.
Stenzel-Poore had created an animal model of chronic stress by altering the mice to overproduce CRF.


















