Shape-shifting mobile devices
29 Apr 2013
The research paper, to be presented on Monday, 29 April, at one of the world's most important conferences on human-computer interfaces will introduce the term 'shape resolution' and its 10 features, to describe the resolution of an interactive device: in addition to display and touch resolution.
 The researchers, led by Dr Anne Roudaut and Professor Sriram Subramanian, from the University of Bristol's Department of Computer Science, have used 'shape resolution' to compare the resolution of six prototypes the team have built using the latest technologies in shape changing material, such as shape memory alloy and electro active polymer.
The researchers, led by Dr Anne Roudaut and Professor Sriram Subramanian, from the University of Bristol's Department of Computer Science, have used 'shape resolution' to compare the resolution of six prototypes the team have built using the latest technologies in shape changing material, such as shape memory alloy and electro active polymer.
One example of a device is the team's concept of Morphees, self-actuated flexible mobile devices that can change shape on-demand to better fit the many services they are likely to support.
The team believes Morphees will be the next generation of mobile devices, where users can download applications that embed a dedicated form factor, for instance the ''stress ball app'' that collapses the device in on itself or the ''game app'' that makes it adopt a console-like shape.
Dr Anne Roudaut, research assistant in the department of computer science's Bristol Interaction and Graphics group, says, ''The interesting thing about our work is that we are a step towards enabling our mobile devices to change shape on-demand.
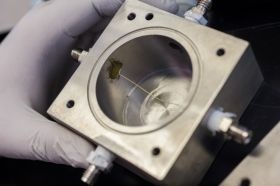 |
| A high-fidelity prototype using projection and tracking on wood tiles that are actuated with thin shape-memory alloy wires |
The device could also transform into a sphere to serve as a stress ball, or bend itself to hide the screen when a password is being typed so passers-by can't see private information.''
By comparing the shape resolution of their prototypes, the researchers have created insights to help designers towards creating high shape resolution Morphees.
In the future the team hope to build higher shape resolution Morphees by investigating the flexibility of materials. They are also interested in exploring other kinds of deformations that the prototypes did not explore, such as porosity and stretchability.


















