New coating may help joint replacements bond better with bone
30 Jul 2013
Broken bones and joint replacements may someday heal faster, thanks to an unusual coating for medical implants under development at The Ohio State University.
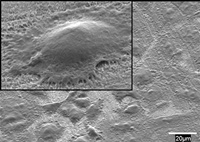 | |
| Cells show signs of healthy growth in this transmission electron microscope image, taken 15 hours after the cells were placed on a titanium surface coated with a carpet of tiny nanowires. In the inset (upper left), filaments can be seen reaching out from cells to the surface, which indicates a strong connection. Image courtesy of Sheikh Akbar, Ohio State University. |
Researchers have found that bone cells grow and reproduce faster on a textured surface than they do on a smooth one - and they grow best when they can cling to a microscopic shag carpet made of tiny metal oxide wires.
In tests, the wires boosted cell growth by nearly 80 per cent compared to other surfaces, which suggests that the coating would help healthy bone form a strong bond with an implant faster.
The engineers developed an affordable technique for creating the wires, which they describe in a paper in the July 2013 issue of the journal Ceramics International.
''What's really exciting about this technique is that we don't have to carve the nanowires from a solid piece of metal or alloy. We can grow them from scratch, by exploiting the physics and chemistry of the materials,'' said Sheikh Akbar, professor of materials science and engineering at Ohio State. ''That's why we call our process 'nanostructures by material design.'''
Akbar's team (co-advised by his colleague, Suliman Dregia, associate professor of materials science and engineering) was able to grow the wires by tailoring the mix of materials and gases inside a furnace. At temperatures around 1,300 degrees Fahrenheit, fine filaments of titanium dioxide rose from a smooth titanium surface. Each was tens of thousands of times smaller than a human hair.
 | |
| Sheikh Akbar |
''It's strange that we don't completely understand why this process works the way it does. We're going to have to do some fancy microscopy to figure it out, but we do know that the wires only form under just the right conditions,'' Akbar said.
In tests, the researchers grew bone cancer cells on three different surfaces - smooth titanium, smooth titanium dioxide, and the nanowire carpet. (They chose the cancer cells because the cells are particularly hardy, and also reproduce the same way healthy bone cells do.)
 | |
| Derek Hansford |
By the end of the study, there were around 90,000 cells per square centimeter on the nanowire surface - 80 per cent more than the 50,000 cells per square centimeter on each of the other two surfaces.
Study co-author Derek Hansford, associate professor of biomedical engineering and materials science and engineering, said that the coating could aid people who have hip and knee replacements, dental implants, or broken bones that require screws and plates to repair them.
"Our hope is that this surface treatment will become a simple-to-implement modification to titanium implants to help them form a stronger interface with surrounding bone tissue."
 | |
| This scanning electron microscope image shows a single wire, tens of thousands of times thinner than a human hair, which was created in a furnace at Ohio State University. Image courtesy of Sheikh Akbar, Ohio State University. |
Akbar believes that the price is right for commercial development. $100 worth of metal foil is enough to make hundreds of samples.
The method to grow the wires is also exceedingly simple. Beyond setting the right mix of materials and gases, it involves little other than pressing a button to turn on the laboratory furnace.
''Seriously, if you spent the day in my lab, you could learn how to do it yourself,'' Akbar said.
He and his team are now exploring other material and gas combinations to make different nano-sized shapes for cell growth and chemical sensing.
This work was partially funded by the National Science Foundation.



















